Abiraterone
Buy Abiraterone online
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ABIRATERONE ACETATE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ABIRATERONE ACETATE TABLETS.
Abiraterone acetate tablet is a CYP17 inhibitor indicated in combination with prednisone for the treatment of patients with
- metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). (1)
- metastatic high-risk castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC)
RXoutreach.org is an online pharmacy that offers Abiraterone at a low cost to individuals who enroll with rxoutreach.org and have a prescription.
DESCRIPTION
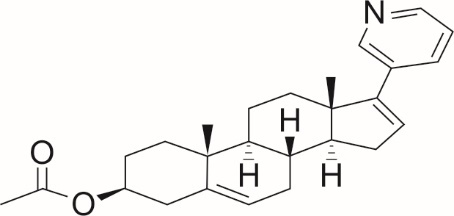
Abiraterone acetate, the active ingredient of abiraterone acetate tablets USP is the acetyl ester of abiraterone. Abiraterone is an inhibitor of CYP17 (17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase). Each abiraterone acetate tablet USP contains 250 mg of abiraterone acetate. Abiraterone is designated chemically as 17-(Pyridin-3-yl)androsta-5,16-dien-3β-yl acetate and its structure is:
Abiraterone acetate appears as a crystalline powder ranging from white to almost white and is not prone to absorbing moisture (non-hygroscopic). It has a chemical structure represented by the formula C 26H 33NO 2, and its molecular weight is 391.55. This compound is lipophilic, exhibiting an octanol-water partition coefficient of 3.57 (Log P). In terms of solubility, abiraterone acetate dissolves readily in methylene chloride, tetrahydrofuran, and toluene. It is also soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, isobutyl methyl ketone, N,N-dimethyl formamide, and acetone. Its solubility is moderate in acetonitrile and dimethyl sulfoxide, limited in hexane, and extremely limited in 0.1N hydrochloride. In water, it is practically insoluble. Additionally, the pKa value of abiraterone acetate is 3.06.
Abiraterone acetate tablets USP are available in 250 mg uncoated tablets with the following inactive ingredients:
• 250 mg uncoated tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium lauryl sulphate.
FDA approved dissolution test specifications differ from USP.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer:
• Abiraterone acetate tablets 1,000 mg orally once daily with prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily.
Metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer:
• Abiraterone acetate tablets 1,000 mg orally once daily with prednisone 5 mg orally once daily.
Patients receiving abiraterone acetate tablets should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog concurrently or should have had bilateral orchiectomy. Abiraterone acetate tablets must be taken as a single dose once daily on an empty stomach.
Do not eat food 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking abiraterone acetate tablets. The tablets must be swallowed whole with water. Do not crush or chew tablets.
Dose Modification:
• For patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), reduce the abiraterone acetate tablets starting dose to 250 mg once daily.
• For patients who develop hepatotoxicity during treatment, hold abiraterone acetate tablets until recovery. Retreatment may be initiated at a reduced dose. Abiraterone acetate tablets should be discontinued if patients develop severe hepatotoxicity.
Customer Information
Abiraterone acetate
(A‐bir‐a‐ter‐one as‐e‐tate)
tablets
What is abiraterone acetate tablet?
Abiraterone acetate tablet is a prescription medicine that is used along with prednisone. Abiraterone acetate tablet is used to treat men with prostate cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
It is not known if abiraterone acetate tablet is safe and effective in females or children.
Inform your healthcare provider about all your health conditions before starting abiraterone acetate tablets, especially if you have:
- Heart issues
- Liver conditions
- Diabetes
- A history of adrenal gland disorders
- A history of pituitary gland disorders
- Current treatments for prostate cancer
- If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Abiraterone acetate tablets can be harmful to an unborn child and may cause pregnancy loss (miscarriage). Women who are or might become pregnant should avoid handling uncoated abiraterone acetate tablets or any damaged tablets without protective measures, such as gloves.
- If your partner is pregnant or might become pregnant. Men with partners who could get pregnant should use effective contraception during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets and for three weeks following the final dose.
- If you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. It's unclear if abiraterone acetate transfers into breast milk.
Also, tell your healthcare provider about all medications and treatments you are using, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements, as abiraterone acetate tablets can interact with many other medications. Do not start or stop any medication without consulting the healthcare provider who prescribed abiraterone acetate tablets. Keep a record of all your medications to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you receive a new prescription.
How should I take abiraterone acetate tablets?
- Take abiraterone acetate tablets and prednisone exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Take your prescribed dose of abiraterone acetate tablets 1 time a day.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed.
- Do not change or stop taking your prescribed dose of abiraterone acetate tablets or prednisone without talking with your healthcare provider first.
- Take abiraterone tablets as a single dose one time a day on an empty stomach. Do not eat food 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking abiraterone tablets.
- Do not take abiraterone acetate tablets with food. Taking abiraterone acetate tablets with food may cause more of the medicine to be absorbed by the body than is needed and this may cause side effects.
- Swallow abiraterone acetate tablets whole. Do not crush or chew tablets.
- Take abiraterone acetate tablets with water.
- If you miss a dose of abiraterone acetate tablets or prednisone, take your prescribed dose the following day. If you miss more than 1 dose, tell your healthcare provider right away.
- Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check for side effects.
What are the possible side effects of abiraterone acetate tablets?
Treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets may lead to severe side effects, such as elevated blood pressure (hypertension), decreased potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia), fluid accumulation (edema), and abnormal heart rhythms. These conditions can be potentially life-threatening. To reduce the risk of these side effects, it's crucial to take prednisone alongside abiraterone acetate tablets exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring is necessary during the treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets, which includes monthly checks of blood pressure, blood tests to monitor potassium levels, and assessments for any indications of fluid retention.
Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of the following symptoms:
o dizziness o confusion
o fast or irregular heartbeats o muscle weakness
o feet faint or lightheaded o pain in your legs
o headache o swelling in your legs or feet
• Adrenal problems may happen if you stop taking prednisone, get an infection, or are under stress.
• Severe l iver problems. You may develop changes in liver function blood tests. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets and during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets. Liver failure may occur, which can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you notice any of the following changes:
o yellowing of the skin or eyes
o darkening of the urine
o severe nausea or vomiting
• Increased risk of bone fracture and death when abiraterone acetate tablets and prednisone or prednisolone, is used in combination with a type of radiation called radium Ra 223 dichloride. Tell your healthcare provider about any other treatments you are taking for prostate cancer.
Severe low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Severe low blood sugar with abiraterone acetate tablets can happen in people who have diabetes and take certain antidiabetic medicines. You and your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar levels regularly during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets and after you stop treatment. Your healthcare provider may also need to change the dose of your antidiabetic medicines.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Uncoated Tablet 250 mg
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess
Abiraterone acetate can lead to increased blood pressure, lowered potassium levels in the blood, and fluid accumulation due to elevated mineralocorticoid levels, which occur as a result of CYP17 enzyme inhibition (refer to Clinical Pharmacology for more details). It's essential to regularly monitor patients for these conditions, ideally once a month. Before initiating and during the course of treatment with abiraterone acetate, controlling high blood pressure and correcting low potassium levels is necessary.
In an analysis of data from four placebo-controlled studies, where patients were given 5 mg of prednisone twice daily along with 1,000 mg of abiraterone acetate daily, it was found that severe hypokalemia (grades 3-4) occurred in 4% of patients treated with abiraterone acetate, compared to 2% in the placebo group. Similarly, severe hypertension (grades 3-4) was observed in 2% of patients in both the abiraterone acetate and placebo groups, and significant fluid retention (grades 3-4) was seen in 1% of patients in each group.
In the LATITUDE trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical study, patients were treated with 5 mg of prednisone daily alongside 1,000 mg of abiraterone acetate daily. In this trial, severe hypokalemia (grades 3-4) was found in 10% of patients receiving abiraterone acetate and 1% of those on the placebo. Severe hypertension (grades 3-4) was observed in 20% of patients on the abiraterone acetate arm compared to 10% on the placebo arm, while significant fluid retention (grades 3-4) was reported in 1% of patients in both groups.
Patients with medical conditions that could be exacerbated by increased blood pressure, hypokalemia, or fluid retention, such as those with heart failure, recent heart attacks, cardiovascular diseases, or ventricular arrhythmias, should be monitored closely. Postmarketing reports have shown that QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes can occur in patients who develop hypokalemia while on abiraterone acetate treatment.
The safety of abiraterone acetate in patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below 50% or with heart failure classified as New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV (in the COU-AA-301 trial) or NYHA Class II to IV (in the COU-AA-302 and LATITUDE trials) is not established, as these patients were not included in these randomized clinical studies (refer to Clinical Studies for more information).
5.2 Adrenocortical Insufficiency
In a combined analysis of five randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies, adrenal insufficiency was observed in 0.3% of the 2,230 patients treated with abiraterone acetate, compared to 0.1% of the 1,763 patients receiving a placebo. Instances of adrenocortical insufficiency have been reported among patients taking abiraterone acetate in conjunction with prednisone, particularly after stopping daily steroid use and/or during times of concurrent infection or stress.
It is important to vigilantly monitor for symptoms and indicators of adrenocortical insufficiency, especially when patients stop taking prednisone, undergo reductions in their prednisone dosage, or are under unusual stress. The symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency may be obscured by side effects related to mineralocorticoid excess that are common in patients undergoing treatment with abiraterone acetate. If adrenocortical insufficiency is suspected, appropriate diagnostic tests should be conducted to confirm the condition. In situations of stress, before, during, and after, an increase in corticosteroid dosage might be necessary (refer to Warnings and Precautions for more details).
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
In the postmarketing phase, severe liver toxicity linked to abiraterone acetate, including cases of fulminant hepatitis, acute liver failure, and fatalities, have been reported (refer to Adverse Reactions for details).
From an analysis of five randomized clinical trials, significant increases in ALT or AST levels (at least five times the upper limit of normal, ULN) were observed in 6% of the 2,230 patients treated with abiraterone acetate, most often within the first three months of starting treatment. Patients with pre-existing elevated ALT or AST levels were at a higher risk of further liver test elevations compared to those with normal baseline values. Due to increases in ALT and AST or abnormal liver function, 1.1% of the 2,230 patients on abiraterone acetate discontinued treatment. No deaths directly attributed to abiraterone acetate due to hepatotoxicity were reported in these trials.
Before initiating abiraterone acetate treatment, measure serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and bilirubin levels, then every two weeks for the first three months and monthly thereafter. For patients with moderate hepatic impairment at baseline and taking a reduced dose of 250 mg abiraterone acetate, check ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels before starting treatment, then weekly for the first month, every two weeks for the next two months, and monthly after that. If signs of hepatotoxicity appear, promptly test for serum total bilirubin, AST, and ALT. Increased monitoring is advised if AST, ALT, or bilirubin levels rise from the patient's baseline. Interrupt abiraterone acetate treatment if AST or ALT levels exceed five times the ULN, or if bilirubin exceeds three times the ULN, and closely monitor liver function.
Consider resuming abiraterone acetate at a reduced dose only after liver function tests return to the patient's baseline or to AST and ALT levels less than or equal to 2.5 times the ULN and total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5 times the ULN (refer to DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section 2.4 for guidelines).
Permanently discontinue abiraterone acetate for patients who experience simultaneous elevations in ALT greater than three times the ULN and total bilirubin greater than two times the ULN without biliary obstruction or other explainable causes (see Dosage and Administration section 2.4).
The safety of restarting abiraterone acetate in patients who experience AST or ALT levels equal to or greater than 20 times the ULN and/or bilirubin levels equal to or greater than 10 times the ULN is not established.
5.4 Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride
Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone is not recommended for use in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride outside of clinical trials.
The clinical efficacy and safety of concurrent initiation of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone and radium Ra 223 dichloride was assessed in a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study (ERA-223 trial) in 806 patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with bone metastases. The study was unblinded early based on an Independent Data Monitoring Committee recommendation.
At the primary analysis, increased incidences of fractures (28.6% vs 11.4%) and deaths (38.5% vs 35.5%) have been observed in patients who received abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride compared to patients who received placebo in combination with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone.
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
The safety and efficacy of abiraterone acetate have not been established in females. Based on animal reproductive studies and mechanism of action, abiraterone acetate can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant female. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of abiraterone acetate to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects at maternal exposures approximately ≥ 0.03 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with abiraterone acetate and for 3 weeks after the last dose of abiraterone acetate [ SEE USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1, 8.3)]. Abiraterone acetate should not be handled by females who are or may become pregnant [ SEE HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING (16)].
5.6 Hypoglycemia
Severe hypoglycemia has been reported when abiraterone acetate was administered to patients with pre-existing diabetes receiving medications containing thiazolidinediones (including pioglitazone) or repaglinide [SEE DRUG INTERACTIONS. Monitor blood glucose in patients with diabetes during and after discontinuation of treatment with abiraterone acetate. Assess if antidiabetic drug dosage needs to be adjusted to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
• Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess.
• Adrenocortical Insufficiency
• Hepatotoxicity
• Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride.
The highlights above do not include all or the complete information needed to use Abiraterone safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Abiraterone. Additional information at https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov